HUD reserve requirements mandate maintaining reserves in specific scenarios, and it’s prudent for homeowners to voluntarily set aside funds for emergencies. Unlike renters who can seek help from their landlord for repairs, homeowners are responsible for maintenance costs. Major system failures like HVAC, electrical, or plumbing can be expensive, often requiring hundreds to thousands of dollars. Lenders can require reserves, which must come from the borrower’s funds and cannot be supplemented with seller concessions or lender credit.
In this guide on HUD reserve requirements, we will cover the mandatory reserve requirements as well as voluntary reserves by homeowners. We will cover the details of HUD reserve requirements and guidelines applicable to FHA loans.
Moreover, appliance breakdowns are common, and it’s usually more cost-effective to replace them than to repair them. In regions with severe winters, such as the Midwest, the breakdown of heating systems can be particularly costly, and contractors typically require immediate payment. Therefore, maintaining a financial reserve is crucial for homeowners to manage unexpected expenses. In the following paragraphs, we will cover the HUD reserve requirements and guidelines on FHA loans.
What is HUD Reserves?
HUD Reserves are funds designated by the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) for specific purposes. These purposes may include maintaining and repairing properties and ensuring the financial stability of the housing programs that HUD oversees.
HUD oversees various housing and community development programs, and these reserve funds help ensure that sufficient resources are available to meet future obligations, emergencies, or unexpected expenditures.
These reserves are crucial for supporting HUD’s objectives, which include ensuring safe and affordable housing, improving communities, and enforcing fair housing laws. The specific nature of these reserves can vary based on the program or initiative they support. For example, in public housing or affordable housing projects, reserves may be used for building repairs, upgrades, or to cover operational deficits during financial stress.
HUD Reserve Requirements Versus Voluntarily Having Reserves
HUD reserve requirements are often viewed by lenders as compensating factors. Insurance does not typically cover maintenance costs, leaving homeowners accountable for any malfunctions or repairs needed in their homes. Generally, HUD, the parent organization of FHA, does not mandate reserves to purchase a single-family home.
There are circumstances where reserves are necessary. Specifically, one month of reserves is mandatory for all manually underwritten loans.
Manual underwriting occurs when the findings from an automated underwriting system are categorized as refer/eligible instead of approve/eligible. Every case designated as refer/eligible by the Automated Underwriting System (AUS) must undergo manual underwriting. In this context, what does having one-month reserves entail?
Need Help Understanding HUD Reserve Requirements for FHA Loans? We Can Guide You!
Contact us today to learn how reserve requirements may impact your FHA loan and get pre-approved.
One-Month Reserves Requirements on FHA Loans
One-month reserves refer to the money required to cover one month of housing expenses. This typically includes the mortgage payment, property taxes, homeowners insurance, and homeowners association (HOA) fees. Lenders sometimes require borrowers to maintain certain reserves, which prove that they can still fulfill their housing responsibilities even in the event of financial challenges, such as sudden expenses or job loss. In the context of a mortgage application, having one-month reserves means that the borrower must show they have enough liquid assets available to pay all housing costs for one month without any additional income. This requirement helps mitigate the lender’s risk by providing a buffer that can prevent default in the short term if the borrower’s financial situation changes.
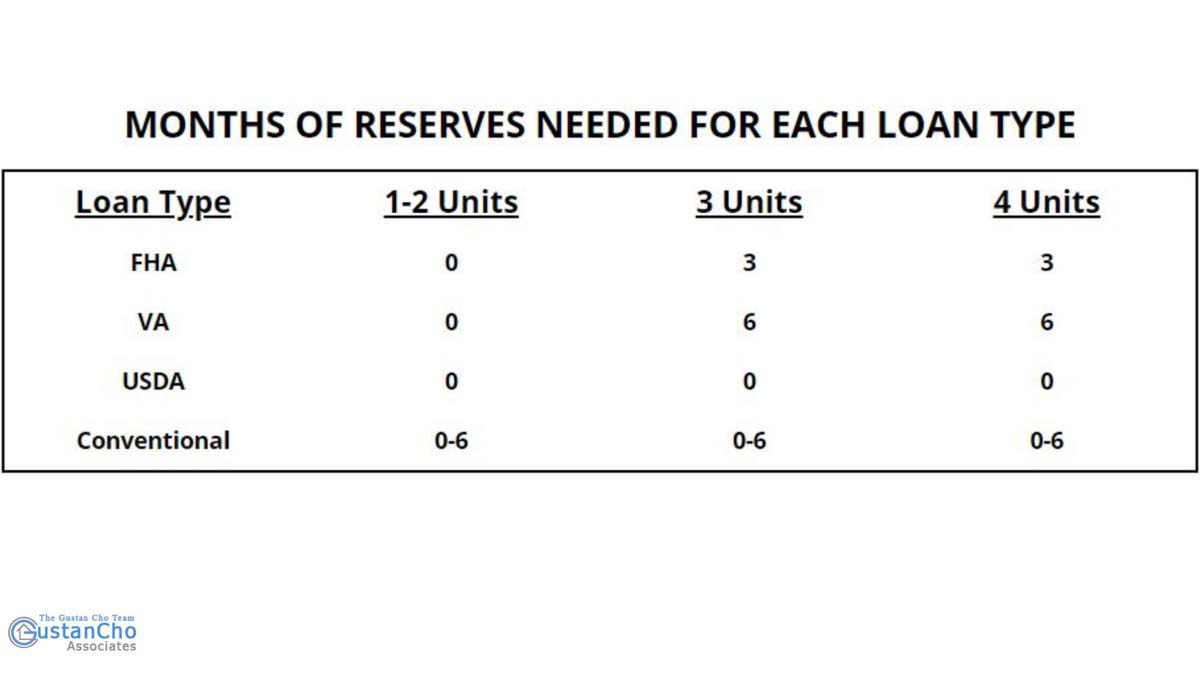
HUD Reserve Requirements on Government and Conventional Mortgages
See the chart below on the reserve requirements on other government loans and conventional mortgages:
There are instances where a mortgage underwriter can condition reserves on a borrower with less than perfect credit. There are other instances where an approve/eligible per AUS borrower can get downgraded to a manual underwrite. Therefore, one month’s reserves are required on manual underwrites.
What Can Be Used For Reserves
HUD Reserve Requirements stipulate that reserves must consist of documented and verifiable sourced funds. These funds should be liquid but cannot be in cash, as they require both sourcing and documentation. Acceptable forms of reserves include:
- Funds in a bank savings account
- Funds in a bank checking account
- Funds in a bank money market account
- Stocks, bonds, and other securities that are liquidatable
- Mutual funds that can be liquidated
- Bank Certificates of Deposit (CDs)
- Accounts receivables due from the Internal Revenue Service
- 60% of the balance from 401k, IRA, thrift savings plans, or Keogh accounts
- Other investment accounts owned by the borrower that are liquid
It is important to note that reserves cannot include gifted or borrowed funds. Additionally, equity in other investment real estate the borrower owns does not qualify as reserves. Likewise, funds from a cash-out refinance transaction are not eligible. A minimum of three months of reserves is required for manually underwritten properties with three to four units.
What is Asset Replacement Reserve?
An asset replacement reserve is a fund established by property owners or managers to finance the future replacement of major components or equipment within a building or facility. This reserve is crucial for handling significant expenditures beyond routine maintenance, which is common in real estate, especially in multi-unit residential buildings, commercial properties, and community associations like condominiums.
Examples include roof replacements, HVAC upgrades, parking lot repaving, or new elevator installations. This reserve ensures that high, often unpredictable costs are spread over time rather than requiring substantial one-time expenditures.
To support these efforts, property owners or stakeholders are typically assessed regularly based on the findings of a reserve study. This study assesses the condition of the property’s major components, forecasts their lifespan, and estimates the replacement costs. By financially preparing for these future needs, the asset replacement reserve not only preserves the property’s value but also guarantees its functionality and safety over the long term.
What are Eligible Replacement Reserve Items?
Eligible replacement reserve items are typically long-lasting components of a property that will require replacement or significant repair as they reach the end of their useful life. The items eligible for inclusion in a replacement reserve fund can vary depending on the property type, the management’s policies, and regulatory guidelines. Still, they generally include major physical parts of the building and common areas that are costly to replace. Here are some common examples:
- Roofing: Replacement or major roof repairs due to aging or wear.
- HVAC Systems: Upgrading or replacing heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems that are no longer efficient or functional.
- Plumbing and Electrical Systems: Major upgrades or replacements of plumbing lines, electrical panels, and wiring.
- Elevators: Overhauling or replacing elevator machinery and related equipment.
- Exterior Painting: Repainting or refinishing the building exterior to maintain structural integrity and aesthetics.
- Paving: Repaving parking areas and driveways that have deteriorated over time.
- Windows and Doors: If your old or damaged windows and doors are no longer energy-efficient or structurally sound, you need to replace them.
- Swimming Pools: Major repairs or replacement of swimming pool components like liners, pumps, or filtration systems.
- Security Systems: Upgrades or replaces outdated security systems, including cameras, gates, and lighting.
These items are planned for and funded through regular assessments of property owners based on the estimated lifespan and replacement costs identified in a comprehensive reserve study. This financial planning tool helps ensure that funds will be available when significant repairs or replacements are necessary without imposing unexpected financial burdens on the property owners.
Ready to Buy a Home with an FHA Loan? Let’s Make Sure You Meet the HUD Reserve Requirements!
Contact us now to learn how we can help you meet these requirements and secure your mortgage.
What is a Reserve for Replacement Component Analysis?
A reserve for replacement component analysis, commonly known as a reserve study, is an essential evaluation determining the funding for major repairs and replacements of common area components in properties like condominiums, homeowners associations, and commercial buildings.
This process begins with a component inventory to identify all elements requiring maintenance, such as roofs, paving, HVAC systems, pools, and elevators.
Following this, a condition assessment is performed to evaluate the current state of each component and estimate its remaining useful life, often with the help of professionals who inspect and compare these elements against industry standards. The analysis also includes cost estimating, where current and future costs for repairing or replacing each component are calculated, considering factors like inflation.
Lender With HUD Reserve Requirements and Guidelines with No Overlays
Finally, a funding plan is developed to determine how much should be regularly contributed to the reserve fund annually to ensure adequate funds are available for future needs without financially burdening property owners. This comprehensive approach provides a strategic financial plan that maintains the property’s value and functionality, protecting owners’ investments and sustaining the quality of life or business operations for all residents or tenants. If you have any questions about HUD reserve requirements or youneed to qualify for loans with a lender with no overlays on government or conforming loans, please contact us at 800-900-8569. Text us for a faster response, orr email us at alex@gustancho.com. The team at Gustan Cho Associates is available 7 days a week, on evenings, weekends, and holidays.
FAQ: HUD Reserve Requirements And Guidelines On FHA Loans
- 1.What are HUD Reserves? HUD Reserves are funds designated by the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) for specific purposes, including property maintenance and repairs and ensuring the financial stability of housing programs. These reserves are essential for supporting HUD’s objectives, such as safe and affordable housing, community improvement, and fair housing enforcement.
- 2.Why are HUD Reserve Requirements important? Homeowners, especially those with FHA loans, must have financial reserves through HUD Reserve Requirements in certain scenarios. This is essential because homeowners are responsible for all maintenance expenses; unlike renters, dealing with significant system failures can be costly.
- 3.What does having one-month reserves mean? One-month reserves refer to sufficient funds to cover one month of housing expenses, including mortgage payments, property taxes, homeowners insurance, and HOA fees. This requirement helps lenders mitigate risk by ensuring homeowners can meet their obligations in case of financial difficulties.
- 4.Can maintenance costs be covered by insurance? Typically, insurance does not cover maintenance costs, so homeowners must handle these expenses themselves. This includes repairs to home systems like HVAC, electrical, or plumbing, which can be costly.
- 5.What are the requirements for manually underwritten loans? For manually underwritten loans, HUD requires one month of reserves. Manual underwriting is necessary when an automated system categorizes an application as refer/eligible, indicating a need for further review due to potential risks.
- 6.What can be used as reserves according to HUD? According to HUD Reserve Requirements, reserves must be documented, verifiable, and liquid assets. Acceptable reserves include bank accounts, money market funds, stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and certain percentages of retirement accounts. Gifted or borrowed funds, equity in investment properties, or funds from cash-out refinancing do not qualify as reserves.
- 7.What is an Asset Replacement Reserve? An Asset Replacement Reserve is a fund set up by property owners to finance the future replacement of major components or equipment. This reserve is essential for managing significant expenditures, like roof replacements or HVAC upgrades, that go beyond routine maintenance.
- 8.What items are eligible for a Replacement Reserve? Eligible items for a replacement reserve typically include long-lasting property components such as roofing, HVAC systems, plumbing and electrical systems, elevators, and exterior painting. These components require substantial investment and planning to replace or repair.
- 9.What is a Reserve for Replacement Component Analysis? Often part of a reserve study, this analysis involves evaluating major property components to determine necessary funding for repairs and replacements. It includes inventorying components, assessing their condition, estimating repair/replacement costs, and developing a funding plan to ensure sufficient reserve funds without unexpected financial burdens on property owners.
This FAQ provides a concise overview of the key points related to HUD Reserve Requirements and reserve management for homeowners and property managers.
This blog about the HUD Reserve Requirements And Guidelines On FHA Loans was updated on April 23rd, 2024.
Want to Know How FHA Reserve Requirements Affect Your Home Loan? We’re Here to Help!
Reach out now to get the information you need and apply for your mortgage.










I read your blog about acquiring a refi while on a ch. 13 bankruptcy payment plan, My husband and I would appreciate your help or your referral to someone to help us refi the house. We owe 280,000 on it; the market has it listed at 475,000. We would like to get a cash-out of $76,000. We went through a mortgage company who was able to get us approved, but said we would have to pay the ch.13 bk out in full. We could not do that because paying it in full would kick us off the repayment plan we currently have and will be completed within Feb 2023. Can you please help us?
Of course, we can definitely help. Please email your contact information to gcho@gustancho.com or call us at 262-716-8151. Text us for a faster response.
I am in escrow buying a 4 Plexi in Hawaii with an FHA loan. My broker just called and said I now need 9 months of cash reserves instead of 3. They stated that it was changed on October 1st. Is this true? Can you help me. I am trying to keep my deal together. Help.
Please reach out to us at gco@gustancho.com or call us at 262-716-8151. Text us for a faster response.