97 LTV Conventional Versus FHA Loans: Which One Is Right for You?
If you’re like most first-time homebuyers, one of the biggest hurdles standing between you and your dream home is the down payment. With everyday costs like housing, groceries, gas, and family responsibilities, saving up for a house can feel impossible.
Thankfully, low-down-payment loan options like 97 LTV Conventional Loans and FHA Loans are here to make homeownership more accessible for hardworking families.
In this updated guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about 97 LTV Conventional Loans versus FHA Loans so you can make the best decision for your situation. Whether you’re looking to purchase your initial home or simply evaluating different loan choices, this guide will help you understand the ins and outs of both programs.
What Is a 97 LTV Conventional Loan?
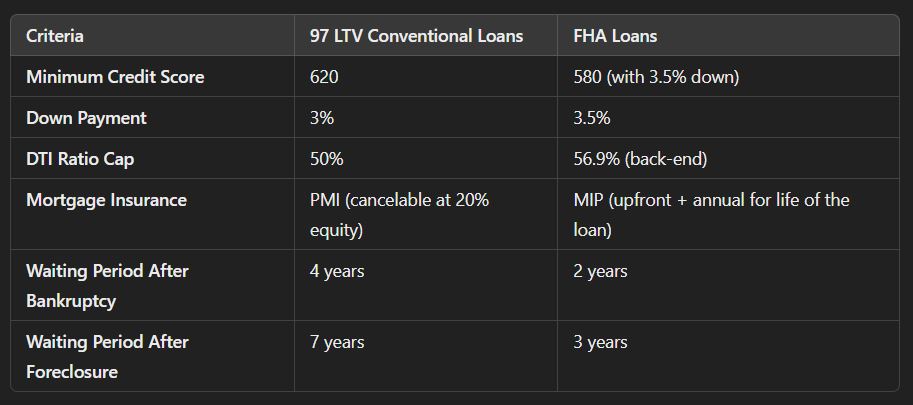
A 97 LTV Conventional Loan is a mortgage program from Fannie Mae that allows you to finance up to 97% of a home’s purchase price. In other words, you only need a 3% down payment to qualify. This loan is tailored to assist individuals purchasing their first home or those who find it challenging to accumulate a substantial down payment.
In contrast to FHA loans, 97 LTV Conventional Loans do not mandate upfront mortgage insurance, potentially reducing your closing costs. The private mortgage insurance (PMI) required for these loans can also be canceled once you’ve built 20% equity in your home.
97% LTV Conventional Loan or FHA Loan? Let’s Find the Right Mortgage for You!
Contact us today to explore the benefits of both 97% LTV Conventional loans and FHA loans and determine which one fits your needs.
What Is an FHA Loan?
FHA Loans are among the most favored choices for those with lower credit ratings or elevated debt-to-income (DTI) ratios. FHA loans require a 3.5% down payment and are known for their lenient eligibility requirements. This makes them a go-to choice for buyers who might not qualify for conventional financing.
FHA loans, unlike 97 LTV Conventional Loans, require borrowers to pay mortgage insurance premiums (MIP). These fees must be settled both upfront and annually for the entire term of the loan. This is a key difference between 97 LTV Conventional versus FHA Loans , is PMI can be canceled on 97 LTV Conventional Loan once enough equity is built.
Key Benefits of 97 LTV Conventional Loans Versus FHA Loans
1. Lower Down Payment Requirement
- 97 LTV Conventional Loans require just a 3% down payment, compared to the 3.5% down payment required by FHA loans.
- This small difference may seem insignificant, but it can save you thousands of dollars upfront, especially if you’re buying a higher-priced home.
2. No Upfront Mortgage Insurance
- FHA loans charge an upfront MIP fee of 1.75% of the loan amount, which is typically rolled into the mortgage balance. This means you’ll pay interest on it for the life of the loan.
- With 97 LTV Conventional Loans, there is no upfront mortgage insurance cost, making it a more affordable option at closing.
3. Ability to Cancel PMI
- FHA loans require lifetime mortgage insurance on less than 10% down loans.
- 97 LTV Conventional Loans, on the other hand, allow you to cancel PMI once you’ve reached 20% equity in your home. This can significantly reduce your monthly payments over time.
4. Better for Borrowers With Strong Credit
- If you have 680 or higher credit score, 97 LTV Conventional Loans often have lower interest rates and PMI costs than FHA loans.
FHA loans, with their more flexible underwriting guidelines, are better suited for borrowers with credit scores between 580 and 679.
Eligibility Requirements for 97 LTV Conventional Loans Versus FHA Loans
Choosing the Right Loan for Your Needs
Here’s how to determine whether a 97 LTV Conventional Loan or an FHA Loan is better for your situation:
Choose a 97 LTV Conventional Loan If…
- You have a credit score of 620 or higher.
- You want to avoid upfront mortgage insurance fees.
- You prefer to cancel PMI once you reach 20% equity.
- Your DTI ratio is under 50%.
- You have no recent bankruptcies, foreclosures, or short sales.
Choose an FHA Loan If…
- Your credit score is 580 to 620.
- You have a higher DTI ratio (up to 56.9% back-end).
- You need a more flexible underwriting process.
- You’re dealing with recent credit issues, such as bankruptcy or foreclosure.
You’re looking for a loan with lenient income verification requirements.
Cost Breakdown: Mortgage Insurance
One of the most significant differences between these two loan options is how mortgage insurance works.
97 LTV Conventional Loan Mortgage Insurance
- Private Mortgage Insurance (PMI): Required if your down payment is less than 20%.
- PMI Cancellation: PMI can be removed once you reach 20% equity.
- Cost: PMI costs vary based on your credit score but are typically lower for borrowers with good credit.
FHA Loan Mortgage Insurance
- Upfront MIP: 1.75% of the loan amount, added to your loan balance.
- Annual MIP: 0.55% of the loan amount, paid for the life of the loan (on 30-year fixed mortgages).
- Cost: While HUD sets MIP rates, they can be higher than PMI over the life of the loan.
2024 Updates for FHA and 97 LTV Conventional Loans
In 2024, there are a few updates you should know about:
- Lower FHA Mortgage Insurance Premiums
- HUD has reduced the annual MIP for FHA loans to 0.55%, down from 0.85%. This helps make FHA loans more affordable.
- Income-Based Repayment Plans for Student Loans
- Both FHA and conventional loans now allow income-based repayment (IBR) amounts to be used for student loan calculations. This can lower your DTI ratio and improve your chances of qualifying.
- If the monthly debt does not report to credit bureaus, the lender can do a rapid rescore and credit supplement and report it to bureaus in 3 to 5 days. Borrowers with higher student loan balances may need to go FHA versus conventional loans.
- Increased Loan Limits
In 2024, both FHA and conventional loans will feature increased loan limits, facilitating home financing in expensive regions.
Real-Life Example: Comparing 97 LTV Conventional Versus FHA Loans
Let’s look at an example to see how these loans stack up.
Scenario:
- Home price: $300,000
- Down payment: 3% (conventional) vs. 3.5% (FHA)
- Credit score: 700
- DTI ratio: 45%
97 LTV Conventional Loan
- Down payment: $9,000
- PMI: $120/month (estimated)
- No upfront mortgage insurance.
- Total monthly payment: ~$1,800 (including taxes and insurance).
FHA Loan
- Down payment: $10,500
- Upfront MIP: $5,250 (rolled into the loan).
- Annual MIP: $125/month.
- Total monthly payment: ~$1,850 (including taxes and insurance).
Result:
In this example, the 97 LTV Conventional Loan offers lower upfront costs and a slightly lower monthly payment, making it the better option for borrowers with good credit.
Confused Between 97% LTV Conventional and FHA Loans? Let Us Help You Decide!
Reach out today to get expert guidance and see which option works best for your home buying goals.
Final Thoughts: Which Loan Should You Choose?
Both 97 LTV Conventional Loans and FHA Loans have their benefits. The right loan for you will depend on your credit score, financial situation, and long-term goals. If you’re looking to minimize upfront costs and want the option to cancel mortgage insurance in the future, the 97 LTV Conventional Loan may be the way to go. However, an FHA Loan could be your best bet if your credit score or DTI ratio makes conventional financing challenging.
Still trying to decide which loan is right for you? Let us help! Our team of experienced mortgage professionals at Gustan Cho Associates can guide you through the process and help you find the best loan for your needs. We’re here to help 7 days a week, including evenings, weekends, and holidays.
Ready to Get Started?
Whether buying your first home or refinancing, choosing the right loan is one of the most important steps in your homeownership journey. Contact Gustan Cho Associates today at 800-900-8569, text us for a faster response, or email us at alex@gustancho.com. Let us help you find the loan that works best for you.
Frequently Asked Questions About 97 LTV Conventional Versus FHA Loans:
Q: What is the Main Difference Between 97 LTV Conventional Loans and FHA Loans?
A: The biggest difference is the down payment and mortgage insurance. A 97 LTV Conventional Loan requires only 3% down and allows you to cancel private mortgage insurance (PMI) once you have 20% equity. FHA Loans require a 3.5% down payment and lifetime mortgage insurance if you put down less than 10%.
Q: Which Loan is Better for Someone With a Low Credit Score?
A: FHA Loans are better for borrowers with lower credit scores, as they allow scores as low as 580 with a 3.5% down payment. A 97 LTV Conventional Loan requires at least a 620 credit score.
Q: Can I Cancel Mortgage Insurance on a 97 LTV Conventional Loan?
A: Absolutely! For a Conventional Loan, PMI can be eliminated once you accumulate 20% equity in your property. Conversely, FHA Loans require mortgage insurance for the full term unless a down payment of 10% or more is made.
Q: What Does “97 LTV” Mean?
A: “97 LTV” stands for a 97% Loan-to-Value ratio, meaning you can borrow up to 97% of the home’s purchase price. This leaves you with just a 3% down payment.
Q: Are 97 LTV Conventional Loans Only for First-Time Homebuyers?
A: Not necessarily. While these loans are designed to help first-time buyers, other borrowers who meet the criteria can also qualify for 97 LTV Conventional Loans.
Q: How Does Mortgage Insurance Differ for 97 LTV Conventional Loans Versus FHA Loans?
A: FHA Loans need an upfront mortgage insurance premium (MIP) and annual premiums for the entire loan period. In contrast, Conventional Loans only need private mortgage insurance (PMI), which you can cancel once you have 20% equity.
Q: What are the Debt-to-Income (DTI) Requirements for These Loans?
A: The maximum DTI for 97 LTV Conventional Loans is 50%. FHA Loans allow a higher DTI ratio of up to 56.9%, making them more flexible for borrowers with higher monthly debts.
Q: Which Loan has Lower Upfront Costs?
A: A 97 LTV Conventional Loan typically has lower upfront costs since it does not require an upfront MIP like FHA Loans. This can make it a better option if you’re short on cash for closing.
Q: What are the Waiting Periods After Bankruptcy or Foreclosure for These Loans?
A: For 97 LTV Conventional Loans, there’s a 4-year waiting period after bankruptcy and a 7-year wait after foreclosure. FHA Loans only require a 2-year wait after bankruptcy and a 3-year wait after foreclosure.
Q: How Do I Decide Between 97 LTV Conventional Loans and FHA Loans?
A: It depends on your financial situation. If you have strong credit and want to cancel mortgage insurance, a 97 LTV Conventional Loan may be the better choice. An FHA Loan might work better if your credit score is lower or you have a high DTI. Always consult with a mortgage expert to weigh your options.
This blog about “Comparison of 97 LTV Conventional Versus FHA Loans” was updated on November 14th, 2024.
Looking to Buy a Home with Only 3% Down? Compare 97% LTV Conventional vs. FHA Loans!
Contact us today to explore your mortgage options and get pre-approved.